자바와 JUnit을 활용한 실용주의 단위 테스트
JUnit 을 활용하여 단위 테스트를 구축하고,
유지보수 자동 빌드 시 수정된 소스로 인한 기존 서비스에 영향이 없는지를 시스템 화 하고 싶다.
자바와 ‘JUnit을 활용한 실용주의 단위 테스트’ 책과 JUnit 버전 문제로 구글에서 따로 서치한 내용을 함께 서술했다.
JUnit5 설정
build.gradle 에 아래 내용 추가
testImplementation ('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') {
exclude group: 'org.junit.vintage', module: 'junit-vintage-engine' //Junit4제외
}
// JUnit5
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.8.2' // 테스트 코드 작성에 필요한 API 제공
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.8.2' // Jupiter API로 작성한 테스트를 위한 엔진 모듈
dependencies {} 아래 내용 없으면 추가
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
테스트 코드 생성 방법 (IntelliJ 기준)
생성하고자 하는 클래스명에서 Alt + Enter 후 Create Test 선택
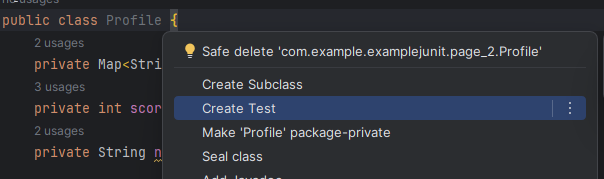
이후 나오는 팝업에서 클래스명, 패키지, 생성하고자 하는 매서드를 선택하여 OK
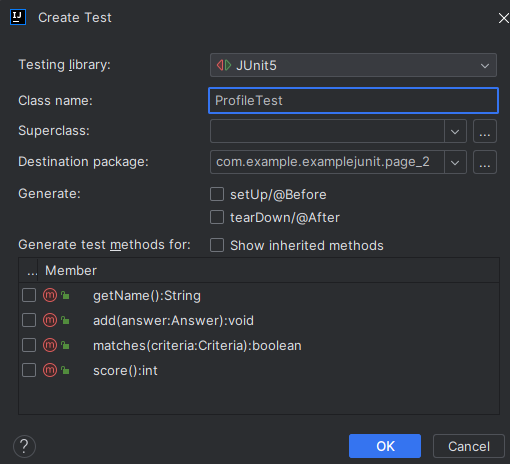
이후 test패키지 내에 생성된 테스트코드 확인 가능
생성된 테스트 클래스 내 테스트 메서드는 기본적으로 @Test 어노테이션을 붙여야 실행됩니다.
@Test
public void matchAnswersFalseWhenMustMatchCriteriaNotMet() {
// 실행 코드
}
Test 전체 공통 초기화하기
Test 클래스 내 공통으로 초기화 할 내용을 @BeforeEach 어노테이션 메서드 내에서 처리하면 @Test 메서드가 더 간결해진다.
@BeforeEach
public void create(){
profile = new Profile("KSY, Inc.");
question = new BooleanQuestion(1, "Got bonus?");
criteria = new Criteria();
}
JUnit 5 에서는 @Before 애노테이션 대신 @BeforeEach 애노테이션을 사용
class ProfileTest {
private Profile profile;
private BooleanQuestion question;
private Criteria criteria;
@BeforeEach
public void create(){
profile = new Profile("KSY, Inc.");
question = new BooleanQuestion(1, "Got bonus?");
criteria = new Criteria();
}
@Test
public void matchAnswersFalseWhenMustMatchCriteriaNotMet() {
Answer profileAnswer = new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE);
profile.add(profileAnswer);
Answer criteriaAnswer = new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE);
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(criteriaAnswer, Weight.MustMatch);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertFalse(matches);
}
@Test
public void matchAnswersTrueForAnyDontCareCriteria() {
Answer profileAnswer = new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE);
profile.add(profileAnswer);
Answer criteriaAnswer = new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE);
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(criteriaAnswer, Weight.DontCare);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertTrue(matches);
}
위 코드에서 흐름은 다음과 같다.
- JUnit이 새로운 ProfileTest 인스턴스 생성
@BeforeEach메서드를 호출하여profile,question,criteria를 초기화matchAnswersFalseWhenMustMatchCriteriaNotMet실행 후 결과 표시- 다시 ProfileTest 인스턴스 생성
@BeforeEach메서드를 호출하여profile,question,criteria를 초기화matchAnswersTrueForAnyDontCareCriteria실행 후 결과 표시
※ 주의 : 테스트 클래스 내 static 필드가 존재한다면 새로운 인스턴스를 생성해도 상태가 공유
JUnit 단언
단언이란 테스트에 넣을 수 있는 정적 메서드 호출이다.
각 단언한 조건이 참인지 검증하여 참이 아니면 테스트는 그 자리에서 멈추고 실패를 보고한다.
JUnit 은 두가지 주요 단언 스타일을 제공하는데,
전통적인 스타일 단언은 JUnit 원래 버전에 포함되어있으며,
새롭고 좀 더 표현력이 좋은 햄크레스트라고 알려진 단언이 존재한다.
(햄크레스트 => matchers 단어의 철자 순서를 바꾼말)
두가지를 섞어서 사용 할 수 있으나 보통 한가지를 선택하는게 좋다.
전통적인 단언
assertTrue
내용이 true 일 때만 성공
@Test
public void assertTrueTest(){
boolean testVal = true;
assertTrue(testVal); // 매개변수가 참일때만 성공
int x = 50;
assertTrue(x > 40); // 조건이 참이므로 성공
}
이외에도 assertFalse 등이 존재한다.
중요한 햄크레스트 매처 살펴보기
JUnit에 포함되어있는 햄크레스트 CoreMatchers 클래스는 바로 매처를 시작할 수 있는 매처 모음을 제공한다.
많은 매처를 사용할수록 테스트 코드의 표현력은 깊어진다.
assertThat
명확한 값을 비교
@Test
public void assertThatTest(){
assertThat(1).isEqualTo(1); // assertThat의 변수와 isEqualsTo의 변수를 일치하는지 비교한다.
}
메시지 작성하기 - 실패 시
// 햄크레스트 단언 : 비교
@Test
public void assertThatTest(){
assertThat(2).as("변수가 1이 아닌가?").isEqualTo(1);
}
실행결과
org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError: [변수가 1이 아닌가?]
expected: 1
but was: 2
Expected :1
Actual :2
예외 던지기
만들어둔 메서드에서 예외를 적절히 던지는지 테스트 할 수 있다.
@Test
public void throwsExceptionTest(){
assertThrows(RuntimeException.class, () -> {
Account.makeException(); // 무조건 오류를 호출하는 함수
});
}
assertThrows(RuntimeException.class... 는 실행하는 함수에서 RuntimeException이 발생하면 성공한다는 의미이다.
이를 이용해 예외가 적절히 발생하는지 테스트 할 수 있다.
오류 메시지 검증
또한 오류 메시지가 원하던 내용인지도 확인 할 수 있다.
@Test
public void exceptionMessageTest(){
RuntimeException e = assertThrows(RuntimeException.class, () -> {
Account.makeException(); // 무조건 오류를 호출하는 함수
});
assertThat(e.getMessage()).isEqualTo("무조건 오류"); // 오류 메시지가 무조건 오류 와 일치해야만 통과
}
오류 규칙(AOP와 유사한 기능)
@ExtendWith(MyExtension.class)
class AccountTest {
@Test
public void test(){
// 테스트 내용 수행
}
}
class MyExtension implements BeforeAllCallback, BeforeEachCallback {
@Override
public void beforeAll(ExtensionContext context) throws Exception {
// 모든 테스트 전 한번 수행
System.out.println("beforeAll");
}
@Override
public void beforeEach(ExtensionContext context) throws Exception {
// 각 테스트 메소드 실행 전에 수행할 작업
System.out.println("beforeEach");
}
}
MyExtension 클래스에서 상속받은 메서드 내용을 구현하여 테스트 실행 전,후 등 이벤트에서 로그출력 등의 내용을 수행할 수 있다. (AOP와 유사)
테스트의 가독성을 높이는 방법
다수의 케이스를 별도의 JUnit 테스트 메서드로 분리하라.
그리고 각각 역할의 이름을 붙여라
@Test
public void allTest(){
// test 1
profile.add(new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE));
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE), Weight.MustMatch);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertFalse(matches);
//test 2
profile.add(new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE));
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE), Weight.DontCare);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertTrue(matches);
}
위 코드 보다 아래 코드가 낫다는 뜻
@Test
public void matchAnswersFalseWhenMustMatchCriteriaNotMet() {
profile.add(new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE));
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE), Weight.MustMatch);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertFalse(matches);
}
@Test
public void matchAnswersTrueForAnyDontCareCriteria() {
profile.add(new Answer(question, Bool.FALSE));
Criterion criterion = new Criterion(new Answer(question, Bool.TRUE), Weight.DontCare);
criteria.add(criterion);
boolean matches = profile.matches(criteria);
assertTrue(matches);
}
테스트 이름을 일관성 있고 좀 더 구체적으로 하라
여기선 메서드 명이 길어져도 일관성 있는 원인과 결과를 넣어 만들라고 했는데(given-when-then 양식)
@DisplayName을 이용하여 한글로 표현해도 될 것 같다.
@Before, @After 메서드로 공통 초기화 분리하기
@Before 과 @After는 각 테스트 매서드 실행 전후로 실행되는 메서드이다.
@Before > @Test > @After > @Before > @Test > @After : 테스트 메서드가 2개 존재한다면 @Before, @After도 두번씩 불린다.
※ 매번 초기화 외에 테스트 클래스 내 한번만 초기화가 필요하다면 @BeforeAll , @AfterAll 을 사용할 수 있다.
테스트 제외하기
현재 수정할 수 없거나 아직 개발이 완료되지 않는 부분의 테스트 코드는 제외처리 할 수 있다.
@Test
@Disabled("to be continue")
public void errorTest() throws RuntimeException { // throws를 넣어도 오류가 무시되지 않는다. JUnit4에서만 가능한듯
RuntimeException e = assertThrows(RuntimeException.class, () -> {
Account.makeException(); // 무조건 오류를 호출하는 함수
});
}
테스트 클래스 실행 결과 errorTest()는 중지표시로 성공/실패가 찍히지 않으며, 메시지는 to be continue가 찍혀있다.
중단된 문제로 실패 테스트를 남길 바에는 제외하는게 낫다.
Mock(Mockito) 을 이용하여 Rest API 테스트하기
@WebMvcTest 를 이용한 Controller 테스트
controller 내용
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<String> createTest(@RequestBody FindTestRequest request) throws Exception {
log.info(request.toString());
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(mapper.writeValueAsString(request));
}
}
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebMvcTest
class TestControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
@DisplayName("POST /test")
public void getTest() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
// Given
FindTestRequest request = new FindTestRequest();
request.setName("김서영");
request.setEmail("ggg");
mockMvc.perform(post("/test")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(mapper.writeValueAsString(request)))
.andExpect(status().isOk()) // response status code 가 200이어야한다.
.andDo(print());
}
}
controller에서 무조건 200을 리턴하므로 테스트는 성공이다.
그러나 controller가 아래와 같이 service를 import 하는 순간 오류가 발생한다.
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class TestController {
private final TestService testService;
@PostMapping("/test")
public ResponseEntity<String> createTest(@RequestBody FindTestRequest request) throws Exception {
log.info(request.toString());
testService.postTest();
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(mapper.writeValueAsString(request));
}
}
테스트 실행 결과
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
Parameter 0 of constructor in com.example.examplejunit.page_10.TestController required a bean of type 'com.example.examplejunit.page_10.TestService' that could not be found.
Action:
Consider defining a bean of type 'com.example.examplejunit.page_10.TestService' in your configuration.
com.example.examplejunit.page_10.TestService 빈을 찾지 못했다는 에러 발생
@WebMvcTest 는 웹과 관련된 아래 컴포넌트만 스캔하기 때문이다.
@Controller, @ControllerAdvice, @JsonComponent, Converter, GenericConverter, Filter, HandlerInterceptor
@Import 를 활용하여 Bean 등록하기
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebMvcTest
@Import(TestService.class)
class TestControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
@DisplayName("POST /test")
public void getTest() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
// Given
FindTestRequest request = new FindTestRequest();
request.setName("김서영");
request.setEmail("ggg");
mockMvc.perform(post("/test")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(mapper.writeValueAsString(request)))
.andExpect(status().isOk()) // response status code 가 200이어야한다.
.andDo(print());
}
}
@Import 를 활용해 TestService.class를 강제 주입하였더니 테스트 결과 성공하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
(하지만 번거롭다.)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc 으로 API 통합 테스트하기
나는 API 기능을 테스트 하고 싶기 때문에 Controller-Service-Repository 모두 스캔하여 테스트 해야한다.
그렇다면 @AutoConfigureMockMvc와 @SpringBootTest 를 이용하여 아래와 같이 구성해보자.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest
class TestControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
@DisplayName("POST /test")
public void getTest() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
// Given
FindTestRequest request = new FindTestRequest();
request.setName("김서영");
request.setEmail("ggg");
mockMvc.perform(post("/test")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(mapper.writeValueAsString(request)))
.andExpect(status().isOk()) // response status code 가 200이어야한다.
.andDo(print());
}
}
TestService가 정상적으로 Bean 등록이 되어 성공 결과를 확인 할 수 있다.
@WebMvcTest vs. @AutoConfigureMockMvc
1. 컨텍스트 로딩:
- @WebMvcTest: 웹 계층만 로딩
(@Controller, @ControllerAdvice, @JsonComponent, Converter/GenericConverter, Filter, WebMvcConfigurer, HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 빈만 스캔) - @AutoConfigureMockMvc: 전체 컨텍스트를 로딩할 수도 있고, @WebMvcTest처럼 웹 계층만 로딩할 수도 있음.
@SpringBootTest와 조합해서 사용하면 전체 컨텍스트를 로딩하고 MockMvc를 이용한 통합 테스트 가능
2. 테스트 범위:
- @WebMvcTest: 웹 계층에만 초점을 맞춘 테스트에 적합.
테스트 속도가 빠르고 컨트롤러와 필수 의존성만 모킹해서 간편하게 테스트 가능 - @AutoConfigureMockMvc: 웹 계층뿐만 아니라 필요한 다른 빈도 로딩해서 통합 테스트를 가능.
전체 컨텍스트 로딩 시에는 테스트 속도가 더 느릴 수 있음
3. 결론:
- 대부분의 경우 웹 계층만 테스트하고 싶다면 @WebMvcTest
- 다른 계층의 빈도 함께 테스트해야 한다면 @AutoConfigureMockMvc
import 가 안되는 문제
assertFalse, assertThat 을 사용하려고 썼는데 import가 제대로 되지 않는 문제가 있었다.
다른사람들의 import 문을 가져오면 오류는 또 안난다;;
이럴경우 우선 Assertions.assertFalse 를 자동완성 되는대로 해준 뒤
추가된 import문을 impost static으로 바꿔준 뒤 Assertions.assertFalse -> assertFalse 로 바꿔주면 된다.
정리
JUnit 테스트의 기본 패턴은 Given - When - Then 이다.
- Given: 테스트를 위한 준비 과정
- When: 테스트를 실행하는 과정으로 테스트 내용을 작성
- Then: 테스트를 검증하는 과정으로 테스트 결과 성공/실패를 확인
책의 내용은 JUnit4 기준이고, 내가 테스트 하는 기준은 JUnit5 여서 달라진 문법이 꽤 많았으나,
JUnit에 어떤 기능들이 제공되는지 공부 할 수 있고, 기능을 알기에 4에서 5로 마이그레이션 된 부분만 검색해서 공부하면 충분했다.
JUnit의 기본 규칙을 알고 원하는 테스트 방법을 찾을 수 있었고,
결론적으로 하고 싶은 API 오류 검사를 위해 Mock 을 따로 더 서치하여 나의 JUnit을 완성 하였다.
앞으로의 계획은 솔루션 유지보수 시 휴먼 에러를 줄이기 위해 모든 API를 JUnit Test를 만들어 두고,
자동 빌드 시 Test를 먼저 수행, 오류 시 빌드 실패를 도출하여 유지보수 도중 생긴 문제를 1차 검증 할 수 있도록 할 예정이다.
(@AutoConfigureMockMvc, @SpringBootTest 사용)